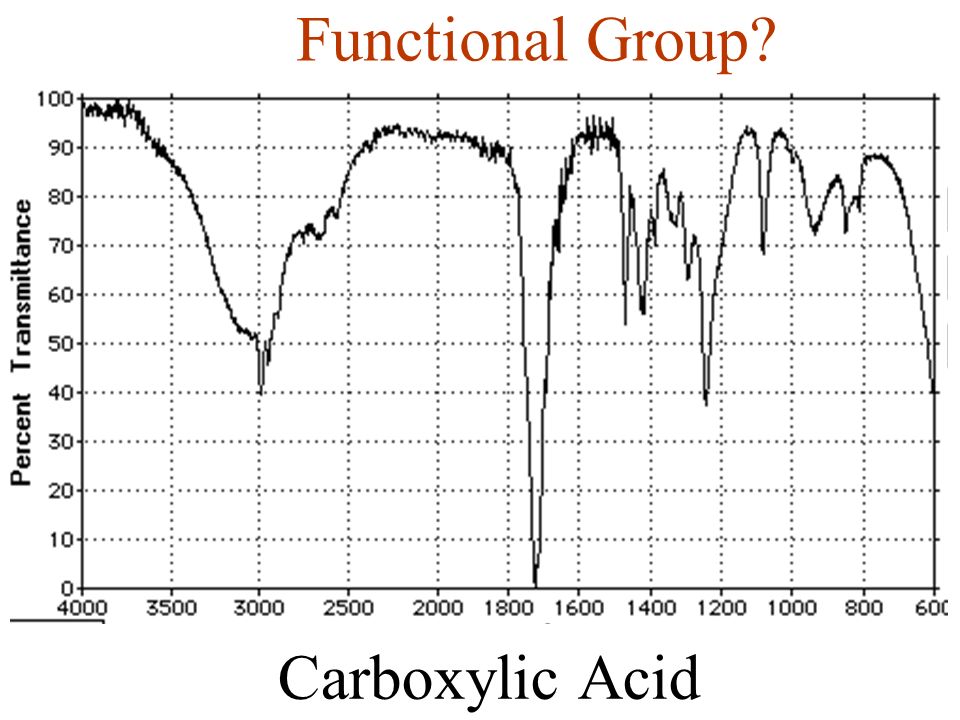
Carboxylic Functional Group

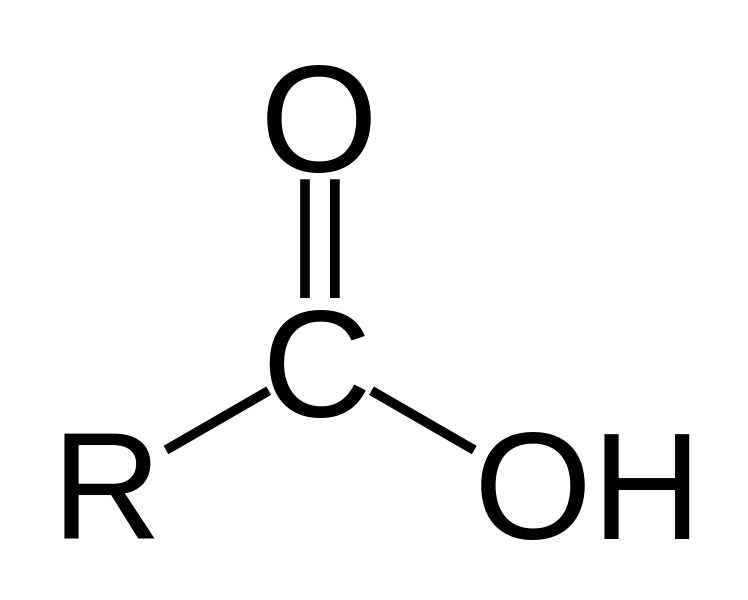
The COOH group is the functional group for carboxylic acids.. Below are links to the structural formulae of carboxylic acids.. Methanoic acid Ethanoic acid. Propanoic acid Butanoic acid. Other examples of carboxylic acids are. 1. Aspirin – taken as a pain killer and to prevent blood clots 2. Citric Acid – found in oranges, lemons and some soft drinks
Carboxylic Acids. The carboxyl functional group that characterizes the carboxylic acids is unusual in that it is composed of two functional groups …
Carboxylic acids are polar.Because they are both hydrogen-bond acceptors (the carbonyl –C=O) and hydrogen-bond donors (the hydroxyl –OH), they also participate in hydrogen bonding.Together the hydroxyl and carbonyl group forms the functional group …


9-1 UNIT (9) CARBOXYLIC ACIDS, ESTERS, AMINES, AND AMIDES 9.1 Carboxylic Acids The functional group in carboxylic acids is called the carboxyl group. A carboxyl group is a carbonyl group (C = O) with a hydroxyl group …

Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 1. Acyl Group Substitution. This is probably the single most important reaction of carboxylic acid derivatives.
Identify the organic class to which the compound belongs. Show all questions <= => ? alcohol ? aldehyde ? amine ? carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid – Synthesis of carboxylic acids: Most of the methods for the synthesis of carboxylic acids can be put into one of two categories: (1) hydrolysis of acid derivatives and (2) oxidation of various compounds. All acid derivatives can be hydrolyzed (cleaved by water) to yield carboxylic acids; the conditions required range from mild …

The Role of Functional Groups. In organic chemistry, a functional group is a specific group of atoms or bonds within a compound that is responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of that compound.

Carboxylic acid: Carboxylic acid, any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon (C) atom is bonded to an oxygen (O) atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group (−OH) by a single bond. A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen (H) atom or to some other univalent combining group. The carboxyl (COOH)

Organic Functional Groups: Aldehydes, ketones, primary alcohols, etc. (Indonesian Translation of this page) Organic chemistry is dominated by the “functional group approach”, where organic molecules are deemed to be constructed from:An inert hydrocarbon skeleton onto which functional groups (FGs) are attached or …